
Hence, the atomic radius decreases across a period. The attraction of the nucleus for the outermost electrons goes on increasing. So, they do not screen the nucleus that much. Atomic radius increases down the group and decreases from left to right in a period. Thus atomic radius increase down a group but reduces from the left to the right across a row. Note: Across a period, the atomic number or the nuclear charge goes on increasing but the electrons are added in the same shell. down a group and from right to left across a period Why The outermost electrons are added to new shells down a group while they are added to the same shell across a row. Hence, the atomic size increases down a group. Nuclear charge increases, so the nuclear attraction on the outer electrons are stronger. This is because: Decreasing reactivity, - Atomic radius increases. As you go down group 7, the halogens become less reactive. As the atomic number increases within a period, the atomic radius decreases. Volatility decreases down the group as the boiling points increase.
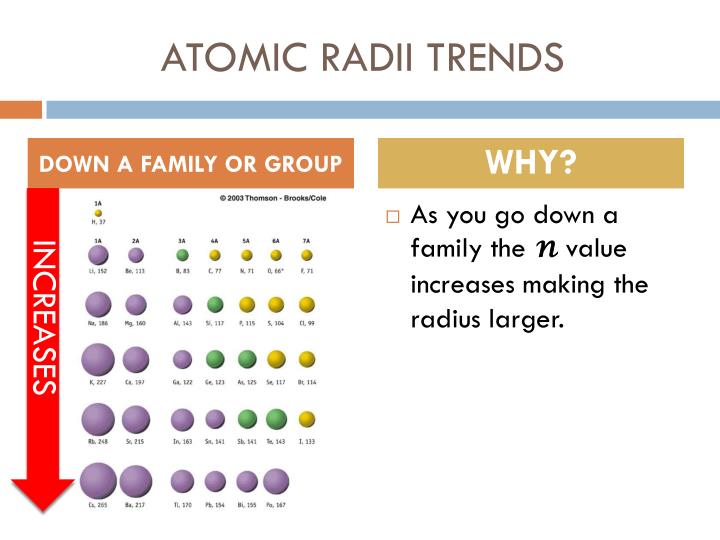
As the atomic number increases down a group, there is again an increase in the positive nuclear charge. Hence, statement I is correct.Īs the atomic number increases from top to bottom in a group, the addition of electrons takes place to new energy levels which lie very far away from the nucleus. The atomic radius of atoms generally increases from top to bottom within a group. Thus, the distance between the nucleus and the last electron will increase and hence, the atomic radius increases down a group. So, the attraction of the nucleus for the outermost shell electron also goes on decreasing. This screening effect due to the addition of new electrons goes on increasing. This increases the atomic radius as the electrons in the outermost shell are further away from the nucleus. 8 years ago how many electrons are filled out in each subshell is 2-8-8-8-8-8. The electrons get added in new shells which will screen the nucleus. Why does the atomic radius increase as you progress down a group As we progress down a group in the periodic table, the number of electrons increases, and so does the number of shells that those electrons are organized into. the simplest answer is that Potassium has higher valence energy level (energy level 4) than Lithium (energy level 2), which has greater distance from the nuclear thus has bigger radius 1 comment ( 7 votes) Upvote Downvote Flag more Show more. Hence, atomic size also increases.Īs we move down a group, the nuclear charge goes on decreasing.

With the increase in the number of orbits, the distance between the last orbit and nucleus also increases. Thus, the electron cloud will move closer to the nucleus and hence atomic size decreases. With the increase in nuclear charge, the force of attraction between the nucleus and electron cloud increases. The factors on which the atomic size depends are nuclear charge and the number of orbits. For main-group elements, the atomic radius increases going down a group because: A. The atomic radius is the most probable distance from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost shell containing electrons. Explanation: As we go across a Period, a row, of the Periodic Table, from left to right as we FACE the Table, we add another positive charge (a proton, a fundamental, positively charged nuclear particle) to the nucleus. \): Comparison of Ionic and Atomic Radius.Hint: An atom is considered to be spherical in size and the size of an atom is measured in terms of its radius. Atomic size INCREASES down a Group, but DECREASES across a Period.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
